Next: Descriptors Up: Characteristic Points Previous: SURF
The latest class of feature point extractors falls under the name of Accelerated Segment Test developed by Rosten. Currently, there are three slightly different versions of this algorithm.
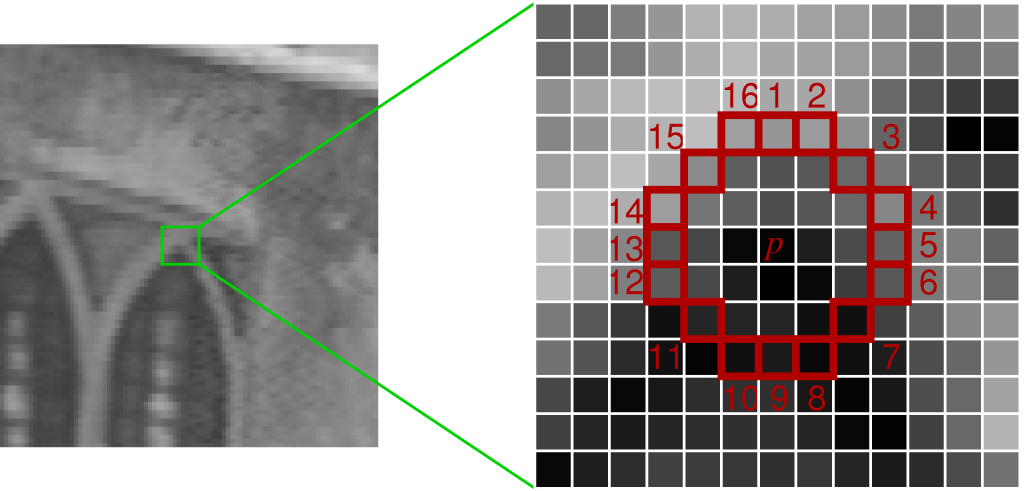 |
The first version of Features from Accelerated Segment Test FAST (RD05) is probably the most intuitive: in this case, points are considered characteristic if they have a continuous sequence of 
This approach has become typical in recent years, as the abundance of public datasets has led to widespread use of classifiers to construct stable feature point detectors. In fact, given primitives that describe the neighborhood of a point, the application of an optimization technique allows for the identification of those that exhibit greater stability for the specific task. The article by Rosten, among other things, provides an excellent survey of previous feature point extraction techniques.
In the latest variant (FAST-ER), the area to be analyzed is extended not only to the points on a circumference but to all the pixels in the vicinity of the central point.
Paolo medici