- Java Standard Edition (JDK)
- Eclipse IDE for Java Developers
- Atom o Notepad++ (o qualsiasi editor di testo)
Programmazione ad oggetti in Java
Alberto Ferrari
Università degli Studi di Parma
Software
Materiale on-line
- Slide del corso
- Documentazione Java
- Testi
- http://www.mindview.net/Books/
- Thinking in Java
- Thinking in Patterns (with Java)
Linguaggi e paradigmi
Linguaggi di programmazione
- Notazione formale per definire algoritmi
- Algoritmo: sequenza di istruzioni che, eseguita, risolve un dato problema in un tempo finito
- Ogni linguaggio è caratterizzato da:
- Sintassi
- Semantica
Sintassi

- Insieme di regole formali per scrivere frasi ben formate (programmi) in un certo linguaggio
- Notazioni formali:
- Backus-Naur Form
- Extended BNF
- Diagrammi sintattici
Semantica
- Attribuisce un significato alle frasi (sintatticamente corrette) costruite nel linguaggio
- Una frase può essere sintatticamente corretta e tuttavia non aver alcun significato
- Soggetto – predicato – complemento
- “La mela mangia il bambino”
- “Il bambino mangia la mela”
- Oppure avere un significato diverso da quello previsto...
- GREEK_PI = 345
Linguaggi di basso livello

- Più orientati alla macchina che ai problemi da trattare
- Linguaggi macchina: solo operazioni eseguibili direttamente dall'elaboratore
- Operazioni molto elementari, diverse per ogni processore, in formato binario
- Linguaggi assembly: prima evoluzione, codici binari → mnemonici
Linguaggi di alto livello
- Introdotti per facilitare la scrittura dei programmi
- Definizione della soluzione in modo intuitivo
- Con una certa astrazione rispetto al calcolatore su cui verranno eseguiti
- Devono essere tradotti in linguaggio macchina
Storia dei linguaggi
The Top 10 (TIOBE 2017)

Paradigmi di sviluppo
- Forniscono la filosofia e la metodologia con cui si scrivono i programmi
- Ogni linguaggio consente (o spinge verso) l'adozione di un particolare paradigma
- Imperativo / procedurale
- Orientato agli oggetti
- Scripting (tipizzazione dinamica, principio Don't Repeat Yourself, DRY)
- Funzionale (funzioni come “cittadini di prima classe”)
- Logico (base di conoscenza + regole di inferenza)
Linguaggi e paradigmi
- Imperativi / procedurali
- Cobol, Fortran, Algol, C, Pascal
- Orientati agli oggetti
- Simula, Smalltalk, Eiffel, C++, Delphi, Java, C#, VB.NET
- Scripting
- Basic, Perl, PHP, Javascript, Python
- Funzionali
- Lisp, Scheme, ML, Haskell, Erlang
- Logici
- Prolog...
Esecuzione dei programmi
- Linguaggio ad alto livello → passi necessari:
- Compilazione, traduzione in linguaggio macchina
- Collegamento con librerie di supporto
- Caricamento in memoria
- Programmi compilati: applicati i 3 passi...
- A tutto il codice; prima dell'esecuzione
- Programmi interpretati: applicati i 3 passi...
- In sequenza, su ogni istruzione; a tempo di esecuzione
Compilazione
- Traduzione da linguaggio ad alto livello a linguaggio macchina
- Analisi: lessicale, grammaticale, contestuale
- Rappresentazione intermedia: albero sintattico
- Generazione codice oggetto
- Codice oggetto: non ancora eseguibile
- Linker, loader
Codice gestito
- Compilazione in codice intermedio
- Bytecode (Java), Common Intermediate Lang. (.NET), …
- Python: compilato per una macchina virtuale (file .pyc), ma in modo trasparente
- Esecuzione su una macchina virtuale, che gestisce la memoria (garbage collection)
- Java Virtual Machine, Common Language Runtime, …
- Spesso compilazione “al volo” (Just In Time) in codice nativo
Java
Cos’è Java
- Insieme di tecnologie
- Linguaggio orientato agli oggetti che semplifica il C++
- Strumenti sia a compile-time che a run-time
- Lancio ufficiale nel 1995
- Piattaforma sviluppata da Sun Microsystems
- Open source dal 2006-07, iniziativa OpenJDK
- Svincolare software da hardware e sistema operativo
- Sistemi web-oriented (Mosaic creato nel 1993)
- Inizialmente lato client, oggi principalmente lato server
- Sistemi embedded (Green group)
- Recentemente, sistemi mobili (smartphone, tablet)
La nascita di Java

- 1991
- James Gosling lavora al “Green Project” (SUN) per studiare la convergenza tra dispositivi di elettronica di consumo e computer
- 1992
- il “Green Project” realizza un palmare che controlla dispositivi di elettronica di consumo con un’interfaccia utente animata e uno schermo sensibile al tocco
- Il dispositivo si chiamava StarSeven ed era programmato mediante un linguaggio totalmente nuovo Oak (quercia) indipendente dal processore �
Oak

- Sintassi di Oak simile al C, ma include il supporto alla programmazione a oggetti
- Gestione degli oggetti più semplice del C++
- La parola chiave di Oak era semplicità di utilizzo e chiarezza della sintassi
- Il prototipo non ebbe molto successo così la tecnologia del Green Project iniziò a essere adattata a Internet e divenne il primo embrione di tecnologia Java �
Java

- Java (nome inglese dell’isola di Giava), è una varietà di caffè. Una bevanda molto utilizzata dai programmatori
- Nel 1995 viene rilasciata la versione 1.0a2 di Java, la prima destinata al pubblico. Il software viene rilasciato completo di sorgenti
- La versione 1.2 di Java viene chiamata Java2 �
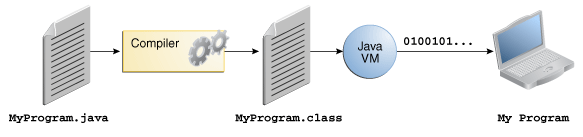
Insieme di tecnologie
- Problema distribuzione su web: programmi strettamente legati ad una piattaforma
- Piattaforma: combinazione di hardware e software di sistema
- Compilatore e bytecode
- Il compilatore Java (
javac) non produce codice eseguibile da una particolare piattaforma, come farebbe un compilatore C - A differenza del linguaggio macchina, il bytecode Java resta uguale per tutte le piattaforme
- Il compilatore Java (
- Macchina virtuale (VM)
- La VM (java) trasforma il bytecode in codice nativo
- Tutti questi pezzi sono denominati assieme come Java
- Compilatore, bytecode, macchina virtuale, librerie, linguaggio ecc.
Ciclo di vita di un’applicazione

Linguaggio semplice
- Sintassi simile al C
- Ma non è una estensione del C, come il C++
- Un compilatore Java non accetta codice C
- Modifiche sostanziali per convertire un programma da C a Java
- Facile da leggere e scrivere (senza errori)
- Codice C medio, al rilascio, ha un bug ogni 55 righe di codice
- Java ha sintassi minima - No “syntactic sugar” (es. operatori)
- Ma più funzionalità del C, grazie all’ampia libreria di classi
- Allocazione e deallocazione automatica della memoria
- Niente
malloc,freee distruttori: metà dei bug in C e C++ legati alla gestione della memoria - Riferimenti controllati: no algebra dei puntatori e accessi arbitrari alla memoria
- Niente
Linguaggio ad oggetti
- Programmazione orientata agli oggetti
- Origini negli anni 1960 – Simula
- Ma diffusione negli anni 1990 – GUI moderne
- Programma: collezione di oggetti che si scambiano messaggi
- Incapsulamento, composizione, ereditarietà, polimorfismo
- Astrazione, programmi più semplici e facili da leggere
- Migliore riuso del codice
- Sviluppo e rilascio più veloce
- Codice modulare, più affidabile e manutenibile
- Java è completamente orientato agli oggetti
- A differenza di Smalltalk, Java ha tipi primitivi
- C++ è ibrido, eredita dal C la scarsa leggibilità (codice offuscato)
Indipendenza dalla piattaforma

- Cross-platform
- Non solo codice sorgente (come C) ma anche bytecode
- Portare programmi Java su una nuova piattaforma
- Portare la macchina virtuale (“interprete”)
- Portare parte delle librerie (AWT, I/O, rete…)
- Compilatore e gran parte delle librerie sono scritte in Java
- Eliminazione di costrutti non specificati o dipendenti dalla piattaforma
- Interi sempre a 32 bit
- Virgola mobile secondo lo standard IEEE 754
Sicurezza
- Verifica del bytecode e sandbox
- Esecuzione sicura di codice scaricato da fonti non fidate
- Le applet non possono accedere al disco o alla rete
- Verifica preventiva sul bytecode dell’applet, controlli a run time
- Al più, una applet può bloccare la VM, ma non l’intero sistema
- No puntatori
- I programmi Java non possono accedere arbitrariamente alla memoria
- Java ha controllo dei tipi forte
- Conversione automatica di un int in long, un byte in short…
- Ma non di un int in boolean
- Controllo su riferimenti e cast tra classi
- Gestione delle eccezioni per errori attesi o inattesi
Buone prestazioni
- Il byte code Java può essere compilato al volo (just-in-time) per ottenere prestazioni simili a codice nativo
- Esistono compilatori Java (es. gcj) che generano codice nativo per una particolare piattaforma (no VM)
- Non si possono limare le prestazioni operando a basso livello come in C, ma si possono ottenere risultati adeguati per molti ambiti
- Grossi programmi scritti in Java
- Eclipse (IDE), Azureus/Vuze (file sharing), HotJava (browser), jEdit (text editor), JBoss (application server), Tomcat (web server), Xerces (parser XML), the Xalan (processore XSLT), javac (compilatore)
Multi-threaded
- Un programma Java può avere diversi thread di esecuzione paralleli
- Java fornisce una API molto semplice per gestire thread
Liberazione automatica della memoria

- Garbage collection: la raccolta della spazzatura di Java
- Non c’è bisogno di allocare o deallocare la memoria esplicitamente
- La memoria è allocata alla creazione di un oggetto, con
new - Viene liberata quando non più utilizzata
- Oggetti sempre in heap
- Costruttori utili per l’inizializzazione
- La memoria è allocata alla creazione di un oggetto, con
- Algoritmi diversi sulle varie VM
- Reference counting: idea di base, ma cicli…
- Mark & sweep: parte da riferimenti locali/globali, marca oggetti raggiungibili
- Generational garbage collection: controlla spesso oggetti recenti
Distruzione degli oggetti
- La creazione di un oggetto richiede memoria per conservare lo stato dell’oggetto
- Quando un oggetto non serve più è necessario liberare questa memoria
- La JVM offre un garbage collector per gestire in modo automatico la restituzione della memoria
- Quando un oggetto non serve più, il garbage collector lo distrugge
- Vantaggi
- Non è possibile dimenticare di liberare la memoria (memory leak)
- Non è possibile liberare dalla memoria oggetti ancora utili (dangling pointer)
- Svantaggi
- Il garbage collector decide autonomamente quando liberare la memoria
- Liberare e compattare la memoria richiede del calcolo
Hello, Java
Metodo main
class HelloWorldApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!"); // Display the string
}
}
- Avvio di un sistema: necessario fornire alla JVM una procedura da eseguire
- Metodo
main
- Metodo
- Ogni classe può definire un metodo
main- A volte, definita classe con solo scopo di contenere
main
- A volte, definita classe con solo scopo di contenere
Compilazione
javac HelloWorldApp.java
- Shell dei comandi, nella cartella contenente il file
.java(source) - Il compilatore genera un file
.class, contenente il bytecode - Possibile specificare una opzione
-classpath- Percorsi dove cercare altre classi necessarie alla compilazione
- Altrimenti usata la variabile d'ambiente
CLASSPATH
Esecuzione
java HelloWorldApp
- Shell dei comandi, nella cartella contenente il file
.class(bytecode) - Comando
java X- Avvio di una nuova JVM
- Esecuzione del metodo
maindella classeX
- Comando
java X arg1 arg 2- Parametri del metodo
main:arg1,arg2ecc. - Spazi usati come separatori tra gli argomenti
- Parametri del metodo
- Possibile specificare una opzione
-classpath...
Eclipse

- Creazione progetto
File-New-Java project- Nome progetto (e package):
hello
- Creazione classe
- Menù contestuale sul progetto
HelloWorldApp, con metodomain
- Esecuzione
- Menù contestuale sulla classe
Run as-Java application
Hello, user
import java.util.Scanner;
class HelloUser {
public static final main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); // to parse user input
System.out.println("Name, age?");
String name = input.next(); // get a word from console
int age = input.nextInt(); // get an int ...
System.out.println("Hello, " + name + ".");
System.out.println("You're " + age + " years old.");
}
}
- Metodo
nextLinediScannerper leggere una intera riga di testo
Tipi primitivi
- Interi, con segno:
byte,short,int,long - Floating point:
float,double - Booleani:
boolean - Caratteri, a 16 bit:
char - Operatori ~ C:
- Assegnamento:
=,+=ecc. - Confronto:
==,!=,<,<=,>,>= - Algebrici:
+,-,*,/,% - Incremento e decremento:
++,--(prefix, postfix) - Logici:
&&,||,!
- Assegnamento:
Stringhe di testo
- Classe e literal
String greeting = "Hello world!";
- Stringhe: sequanze immutabili di caratteri
char c = greeting.charAt(1); // 'e'- Attenzione: la numerazione dei caratteri parte da 0!
- Lunghezza: numero di
charint len = greeting.length();- Ogni
charoccupa 16 bit (codifica UTF-16) - Ma alcuni simboli possono richiedere più
char
- Concatenazione, sia su oggetti che literal
String txt = string1 + string2;- Dietro le quinte, usato il metodo
concatdiString
Caratteri e testo
- Necessaria convenzione per codifica numerica (binaria) dei caratteri
- Codifica ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) a 7 bit
- Caratteri alfanumerici: lettere maiuscole, minuscole, numeri, spazio
- Simboli e punteggiatura: @, #, …
- Caratteri di controllo (non tutti visualizzabili):
TAB, LF, CR, BELLecc. - Interruzione di riga: varie combinazioni di
LFeCRsu diversi sistemi
Tabella ASCII di base
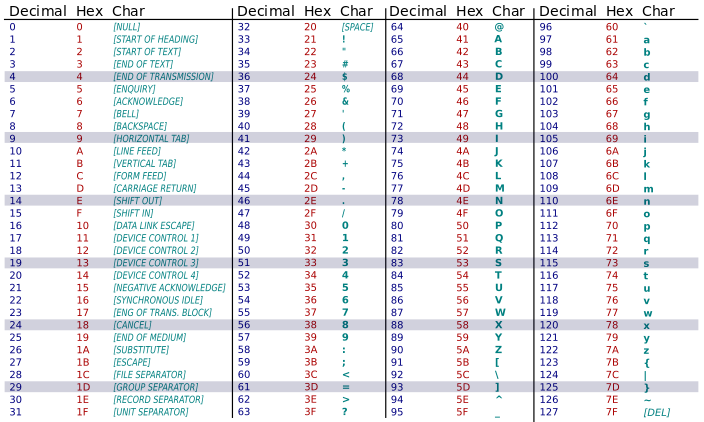
Tabella ASCII estesa

- Caratteri accentati + caratteri per grafici
- Code Page 437 per PC (DOS) in Nord America
- Possibile mischiare testo in inglese e francese (anche se in Francia CP850); ma non assieme greco (CP737), russo ecc.
- ISO 8859, estensioni standard per ASCII ad 8 bit
- ISO 8859-1 (o Latin1): Lingue dell’Europa Occidentale
- ISO 8859-2: Lingue dell’Europa Orientale
- ISO 8859-5: Alfabeto cirillico
- ISO 8859-15: Latin1 con simbolo euro (€)
Unicode


- Unicode associa un preciso code-point (32 bit) a ciascun simbolo
- Possibile rappresentare miliardi di simboli
- Primi 256 code-point = Latin1
- Attualmente >30 sistemi di scrittura
- Rappresentazione di geroglifici e caratteri cuneiformi
- Proposta per Klingon (da Star Trek… rifiutata!)
Selezione: if
int x = input.nextInt();
int y;
if (x >= 0) {
y = x;
System.out.println("" + x + "is positive");
} else {
y = -x
System.out.println("" + x + "is negative");
}
System.out.println("abs = " + y);
Per casi più complessi, esiste anche il costrutto switch-case
Confronto tra parole
- Attenzione all'operatore
==- Confronta il valore di tipi primitivi
- Confronta i riferimenti, non i valori degli oggetti
- Ok per confronto tra interi, ma non tra stringhe
- Metodi
equals(boolean) ecompareTo(-1,0,+1)
String a = input.next(), b = input.next();
if (a.equals(b)) {
System.out.println("The words are equal");
} else if (a.compareTo(b) == -1) {
System.out.println("The words are ordered");
} else {
System.out.println("The words are inverted");
}
Iterazione: while
int total = 0, count = 0;
System.out.println("Val (0 to end)? ");
int val = input.nextInt();
while (val != 0) {
total += val; ++count;
System.out.println("Val (0 to end)? ");
int val = input.nextInt();
}
if (count > 0) {
float avg = total / float(count);
System.out.println("Avg: " + avg);
}
In alternativa, si può usare un ciclo do-while
Array
- Sequenza di elementi, dello stesso tipo
- Ha un nome che lo identifica ed una lunghezza
- Singoli elementi identificati tramite indice numerico
- Indice da 0, fino a
length- 1!
- Indice da 0, fino a
String[] toBuy = {"spam", "eggs", "beans"};
int[] rainfallData = {13, 24, 18, 15};
String[] months = {"Jan", "Feb", "Mar",
"Apr", "May", "Jun",
"Jul", "Aug", "Sep",
"Oct", "Nov", "Dec"};
Uso degli array

// declaration
int[] k;
// creation
k = new int[3];
String[] toBuy = {"spam", "eggs", "beans"};
System.out.println(toBuy.length);
System.out.println(toBuy[1]); // eggs
toBuy[1] = "bacon";
- Lunghezza
- Segnalato errore se indice fuori dai limiti (da 0 a length - 1)
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
ArrayList
- Simile ad un array, ma con dimensione variabile
- Metodi principali:
add, get, set, size
ArrayList<String> toBuy = new ArrayList<>();
toBuy.add("spam");
System.out.println(toBuy.size()); // 1
toBuy.add("eggs");
toBuy.add("beans");
System.out.println(toBuy.size()); // 3
System.out.println(toBuy.get(2)); // beans
toBuy.set(2, "bacon");
System.out.println(toBuy.get(2)); // bacon
// see ArrayList documention
Cicli su collezioni, for
for (int i = 0; i < toBuy.size(); i++) {
String item = toBuy.get(i);
System.out.println(item);
}
for (String item : toBuy) { System.out.println(item); }
int[] rainfallData = {13, 24, 18, 15};
for (int val : rainfallData) { System.out.println(val); }
Cicli e annidamento

int y = in.nextInt();
for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++) {
System.out.format("%4d", x * y);
}
System.out.println();
for (int y = 1; y <= 10; y++) {
for (int x = 1; x <= 10; x++) {
System.out.format("%4d", x * y);
}
System.out.println();
}
Matrice, somma colonne
int[][] matrix = {{2, 4, 3, 8},
{9, 3, 2, 7},
{5, 6, 9, 1}};
int rows = matrix.length;
int cols = matrix[0].length;
for (int x = 0; x < cols; x ++) {
int total = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < rows; y++) {
int val = matrix[y][x];
total += val;
}
System.out.println("Col #" + x + " sums to " + total);
}
Esercizi
Cerchio

- Chiedere all'utente il valore del raggio
rdi un cerchio - Mostrare il valore dell'area e della circonferenza
- Se
rè negativo, però, mostrare un messaggio d'errore
Definire una costante PI = 3.14159
Altrimenti usare Math.PI
Minore e maggiore

- Chiedere all'utente tre numeri interi:
a,b,c - Determinare qual è il minore dei tre
- Determinare qual è il maggiore dei tre
Controllare prima di tutto se a è minore degli altri due
Altrimenti controllare se b è minore di c
Altrimenti ...
Cubi in ciclo

- In un ciclo, ripetere le seguenti operazioni
- Chiedere all'utente un numero
- Mostrare il suo valore al cubo
- Il valore 0 indica il termine della sequenza
Numero segreto

- Generare un intero “segreto” a caso tra 1 e 90
- Chiedere ripetutamente all'utente di immettere un numero, finché non indovina quello generato
- Ogni volta dire se il numero immesso è maggiore o minore del numero segreto
Generatore di numeri pseudo-casuali: Random random = new Random()
Estrazione numero tra 0 e 89: random.nextInt(90)
Conteggio a ritroso

- Leggere un numero positivo
n - Per ciascun valore
ytraned 1... - Stampare una riga con
yripetizioni diy
4444
333
22
1
Usare due cicli for annidati
All'inizio fissare y pari ad un certo valore e scrivere una sola riga; es.: y = 4 → “4444”
Poi racchiudere tutto in un ciclo for esterno, per variare y:
y parte da n, arriva ad 1, ad ogni passo decresce di 1
Conteggio di 0 e 1

- Chiedere una riga di testo all'utente
- Contare separatamente il numero di cifre
0ed1presenti
Usare un ciclo for sulla stringa
Conteggio caratteri

- Chiedere una riga di testo all'utente
- Contare separatamente le occorrenze di ciascuna lettera maiuscola (da
'A'a'Z')
Creare un array di 26 elementi, inizialmente tutti posti a 0
Ciascun elemento è il contatore per una certa lettera
L'indice del contatore corrispondente ad una lettera val può essere ottenuto come val - 'A'
Valore in lista
- Chiedere all'utente una lista di valori interi
- La lista termina quando l'utente inserisce il valore
0
- La lista termina quando l'utente inserisce il valore
- Ripetutamente...
- Chiedere all'utente un valore da cercare
- Contare le occorrenze di quel valore nella lista
Matrice di valori
- Chiedere all'utente
n, il lato di una matrice quadrata- Chiedere all'utente di inserire gli
n2valori della matrice
- Chiedere all'utente di inserire gli
- In seguito, chiedere ripetutamente all'utente un valore
k, da cercare- Comunicare quante volte
kè presente nella matrice - Comunicare inoltre quante volte
kè presente sulle diagonali principali
- Comunicare quante volte
Memory

- Allocare un array di caratteri, di dimensione
rows×cols- L'utente sceglie
rowsecols, però celle in numero pari
- L'utente sceglie
- Inserire in ordine le prime lettere dell'alfabeto, ciascuna ripetuta due volte
- Per ciascuna cella, scegliere una posizione a caso e scambiare il contenuto delle celle
- Mostrare la matrice risultante
Usare un array semplice (anzichè una matrice, array di array)
Andare a capo quando i % cols == cols - 1
Scitala spartana

- Leggere una intero riga di testo
- Inserire in una matrice i primi
COLS×ROWScaratteriCOLScolonne ×ROWSrighe, valori prefissati- Riempire una riga della matrice dopo l'altra
- ltr e ttb (→, ↓)
- Scrivere il contenuto della matrice su console
- Scrivere una colonna della matrice dopo l'altra
- Prima riga su console = prima colonna della matrice...
- ttb e ltr (↓, →)
Usare una matrice (predefinita): char[][] matrix = new char[ROWS][COLS]
Alberto Ferrari
Università degli Studi di Parma