- collections
- iterators
- loops
- arrays

Grouping objects
Alberto Ferrari
Ingegneria dell'Informazione, UniPR
Concepts
Collection
- A collection object can store an arbitrary number of other objects
- The number of items stored in a collection varies:
- Items get added
- Items get deleted
Class libraries
- One of the features of object-oriented languages that makes them powerful is that they are often accompanied by class libraries
- These libraries typically contain many hundreds or thousands of different classes that have proved useful to developers on a wide range of different projects
- Java calls its libraries packages
- We don’t have to write everything from scratch
- The java.util package contains classes for collections of objects �
Features of the collections
- Increases its capacity as necessary
- Keeps a private count
- we can get it using the size() accessor
- Keeps the objects in the order they are added
- Each item has an index
- Index values may change if items are removed (or further items added).
�
- Details of how all this is done are hidden:
- Does that matter?
- Does not knowing how prevent us from using it?
Generic classes
- Collection classes are examples of parameterised or generic classes (types)
- When using collections we have to specify two types: the type of the collection itself and the type of the elements
- Example: type definition ArrayList
can be read as “ArrayList of String”
- Example: type definition ArrayList
ArrayList<Person>
ArrayList<TicketMachine>
ArrayList<String>
- ArrayList is a class of the Java library that provides the simplest possible way of grouping objects, an unsorted but ordered flexible-sized list
- ArrayList implements list functionality:
- it has methods add, get, size, etc.
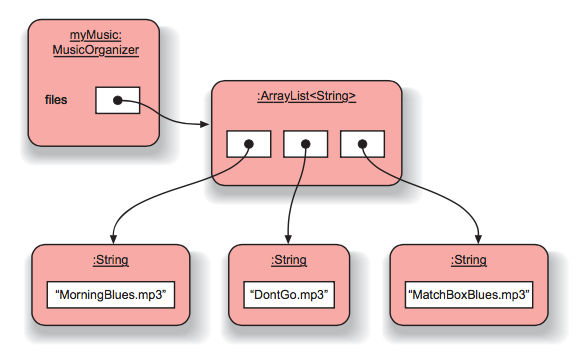
Example: music organizer
- Project music-organizer-v1 will simply work with the file names of individual music tracks
- There will be no separate details of title, artist, playing time, etc
- The ArrayList to store String objects representing the file names
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class MusicOrganizer {
// An ArrayList for storing the file names of music files.
private ArrayList<String> files;
public MusicOrganizer() {
files = new ArrayList<String>();
}
...
Object diagram
Example
Avoid duplication
- An organizer has a getNumberOfFiles method
- An organizer delegates the responsibility for keeping track of the number of items to its ArrayList object
public int getNumberOfFiles() {
return files.size();
}
Numbering with collections

- The first item added to a collection is given index number 0, the second is given index number 1, and so on
- Use method get(int) to access one element of the collection
- If you try to access a collection element that is outside the valid indices of the ArrayList you will get an error message (IndexOutOfBoundsException) and the program will terminate
- Use method remove(int) to remove one element from a collection
- The removal process can change the index values at which other objects in the collection are stored
- It is possible to insert items into an ArrayList at a position other than right at the end of it
Third-party libraries
- a third-party software component is a reusable software component developed to be either freely distributed or sold by an entity other than the original vendor of the development platform.
- Example: MusicPlayer class from javazoom.net in project music-organizer-v2
- MusicPlayer() - Constructor for objects of class MusicFilePlayer
- void playSample(String filename) - Play a part of the given file
- void startPlaying(String filename) - Start playing the given audio file
- void stop() - stop playing
Collections
for-each loop
for-each loop
- A loop can be used to execute a block of statements repeatedly without having to write them multiple times
for(ElementType element : collection) {
loop body
}
- Example
/**
* Show a list of all the files in the collection.
*/
public void listAllFiles() {
for(String filename : files) {
System.out.println(filename);
}
}
Exercise
- Add the void listMatching(String searchSting) method in class MusicOrganizer
to list all file with names that contain searchString
- use java.lang.String.contains() method
- If no file matches the string print a message
- Add method playAll that plays all files that match a search string
- use method playSample of class MusicPlayer
- Add method playFirst that plays the first file that matches a search string
- for-each or while?
while(boolean condition) {
loop body
}
Searching a collection
- The search succeeds after an indefinite number of iterations
- The search fails after exhausting all possibilities
- example
int index = 0;
boolean found = false;
while(index < myCollection.size() && !found) {
myElement = myCollection.get(index);
if (myElement ...) {
found = true;
...
}
index++;
}
Collections of objects
- Look at project music-organizer-v5
// An ArrayList for storing music tracks.
private ArrayList<Track> tracks;
- When listing details of the tracks in listAllTracks, we request the Track object to return a String containing its details
- This shows that we have designed the Track class to be responsible for formatting the details to be printed.
- This is an example of what is called responsibility-driven design
/** Show a list of all the tracks in the collection. */
public void listAllTracks() {
for(Track track : tracks) {
System.out.println(track.getDetails());
}
}
iterators
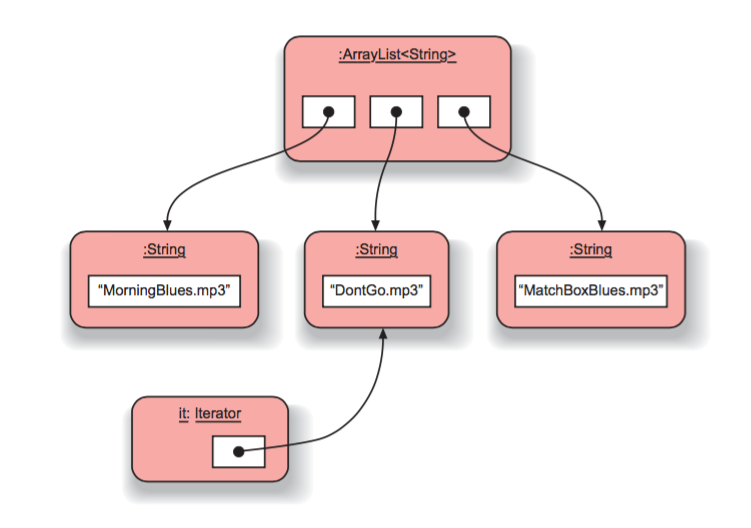
- An iterator is an object that provides functionality to iterate over all elements of a collection
- The iterator method of a collection returns an Iterator object
Iterator<ElementType> it = myCollection.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
// call it.next() to get the next element
// do something with that element
}
Example
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
...
/**
* List all the tracks.
*/
public void listAllTracks() {
Iterator<Track> it = tracks.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Track t = it.next();
System.out.println(t.getDetails());
}
}
Iterator
removing elements
- We couldn't use a for-each loop
- If we try to modify the collection using one of the collection’s remove
methods while in the middle of an iteration, the system will report an error
- ConcurrentModificationException
Iterator<Track> it = tracks.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Track t = it.next();
String artist = t.getArtist();
if(artist.equals(artistToRemove)) {
it.remove();
}
}
� - Use the Iterator remove method not the Collection remove method!
Exercise 1
- Implement the method removeTitle in your music organizer that lets you specify a string as a parameter and then removes all tracks whose titles contain that string
- Implement the method renameTitle in your music organizer that lets you specify two strings as a parameter and then change the first string with the second one in all tracks
Exercise 2
- Use the club project and complete the Club class (the Club class is intended to store Membership objects in a collection) within Club, define a field for an ArrayList create the collection object and assign it to the field.
- Complete the numberOfMembers method to return the current size of the collection
- Complete the join method
Exercise 3
- Define a method in the Club class with the following description:
/**
* Determine the number of members who joined in the given month.
* @param month The month we are interested in.
* @return The number of members who joined in that month.
*/
public int joinedInMonth(int month)
If the month parameter is outside the valid range of 1 to 12, print an error message and return zero.
Exercise 4
- Define a method in the Club class with the following description:
/**
* Remove from the club's collection all members who joined in the given month
* and return them stored in a separate collection object.
* @param month The month of the membership.
* @param year The year of the membership.
* @return The members who joined in the given month and year.
*/
public ArrayList<Membership> purge(int month, int year)
If the month parameter is outside the valid range of 1 to 12, print an error message and return a collection object with no objects stored in it.
Exercise 5
- Write a method in the MusicOrganizer class to select a single random track from its list and play it.
- The java.util package contains the Random class whose nextInt method will generate a positive random integer within a limited range.
- Write a method to play every track in the track list exactly once in random order.
The null keyword
- null is used to mean “no object” when an object variable is not currently referring to a particular object.
- A field that has not explicitly been initialized will contain the value null by default
- If a variable contains the null value, a method call should not be made on it
- NullPointerException
myObject = null;
Anonymous objects
- An anonymous object is an object without a name
myCollection.add(new MyElement());
Fixed-size collections
- array is a special type of collection that can store a fixed number of items
- Advantages:
- Access to items held in array is more efficient than access items in a flexible-size collection
- Arrays are able to store either objects or primitive-type values
- Flexible-size collections can store only objects
Arrays examples
from project weblog-analyzer
...
private int[] hourCounts; //int-array declaration
...
hourCounts = new int[24]; //array of 24 int instantiation
...
for(int hour = 0; hour < hourCounts.length; hour++) {
System.out.println(hour + ": " + hourCounts[hour]); // access elements
}
...
for(int value : hourCounts) {
System.out.println(": " + value); //for-each with arrays
}
Array

Collection: which loop?
- If you need to iterate over all elements in a collection,
the for-each loop is almost always the most elegant loop to use
- but it does not give you a loop counter
- The for loop is good if you know at the start of the loop how many iterations
- it is also very good if you need to use the loop counter explicitly
- The while loop should be preferred if, at the start of the loop, you don’t know how often you need to loop
- If you need to remove elements from the collection
- use a for loop with an Iterator if you want to examine the whole collection
- use a while loop if you might finish before reaching the end of the collection
Exercise 1
- In LogAnalyzer class Complete the numberOfAccesses method to count the total number of accesses recorded in the log file.
- Complete it by using a for loop to iterate over hourCounts:
/**
* Return the number of accesses recorded in the log file.
*/
public int numberOfAccesses() {
int total = 0;
// Add the value in each element of hourCounts to total.
...
return total;
}
Exercise 2
- Add a method busiestHour to LogAnalyzer that returns the busiest hour
- Add a method quietestHour to LogAnalyzer that returns the number of the least busy hour
- Add a method to LogAnalyzer that finds which two-hour period is the busiest
- Return the value of the first hour of this period.
- Extend the log-file format with additional numerical fields. For instance, servers commonly store a numerical code that indicates whether an access was successful or not. The value 200 stands for a successful access, 403 means that access to the document was forbidden, and 404 means that the document could not be found.
- Have the analyzer provide information on the number of successful and unsuccessful accesses.
Concept summary
- collection A collection object can store an arbitrary number of other objects.
- loop A loop can be used to execute a block of statements repeatedly without having to write them multiple times.
- iterator An iterator is an object that provides functionality to iterate over all elements of a collection.
- null null is used to mean “no object” when an object variable is not currently referring to a particular object. A field that has not explicitly been initialized will contain the value null by default.
- array An array is a special type of collection that can store a fixed number of elements.

Alberto Ferrari
Ingegneria dell'Informazione, UniPR
www.ce.unipr.it/~aferrari/